Browse 227,679 greenhouse effect stock photos and images available, or search for greenhouse effect diagram or greenhouse effect illustration to find more great stock photos and pictures Man on a rooftop looks at approaching flames as the Springs fire continues to grow on near Camarillo, California The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directions Part of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming it The intensity of downward radiation – that is, the strength of the greenhouse effect – depends on the amount of greenhousePlus, get full access to a library of over 316 million images Learn more Royaltyfree stock vector ID Greenhouse effect vector illustration diagram Environment pollution problem and fighting climate change Informational infographic for education and rising awareness Human industrial activity issue
Climate Change Silence Is Ignorance Really Bliss Early Career Ecologists
Green house greenhouse effect diagram drawing
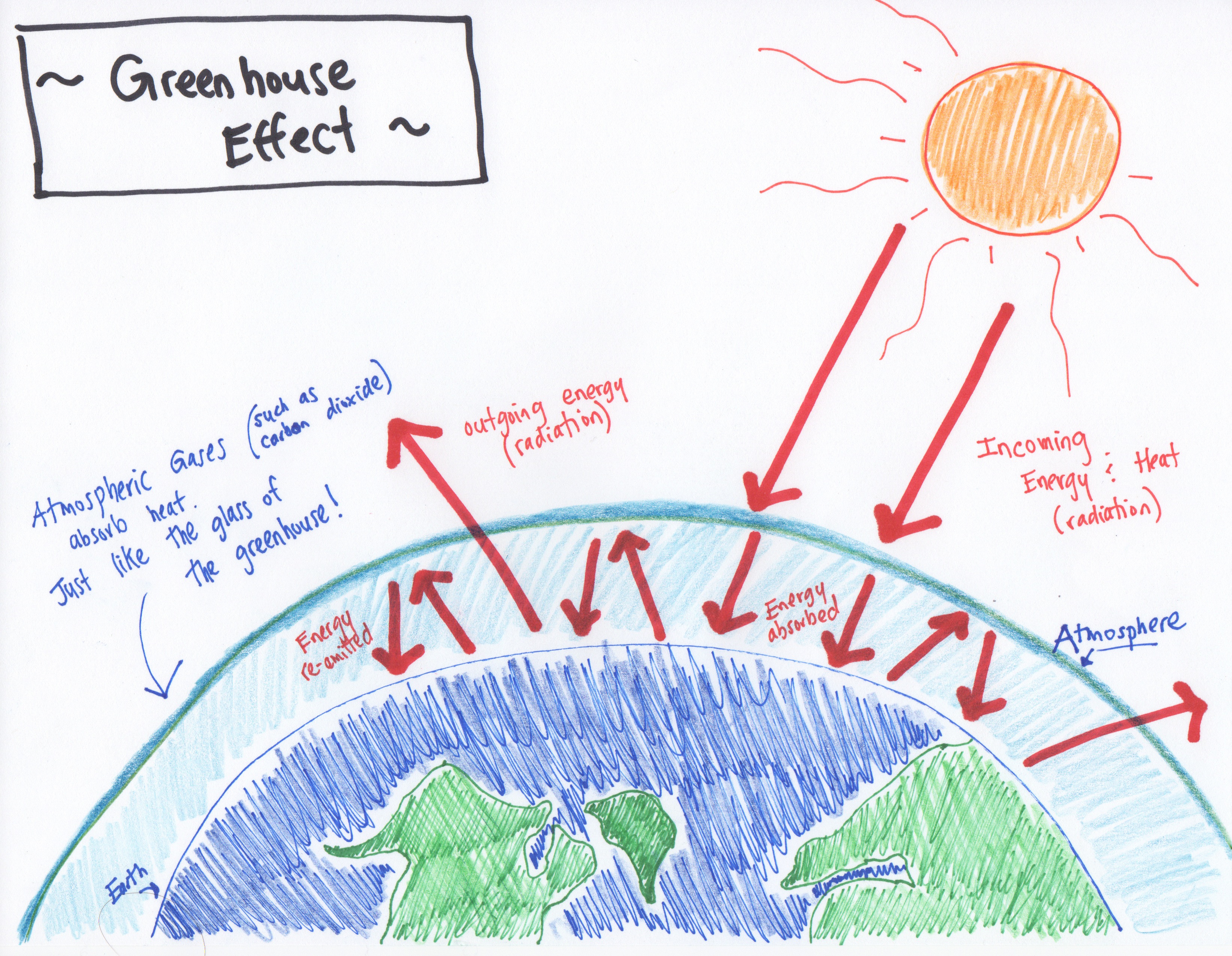
Green house greenhouse effect diagram drawing-Surrounding the greenhouse effect and global warming Here's how you can help Task 1 Draw a diagram illustrating the greenhouse effect Label it carefully Task 2 Below your diagram write a concise paragraph that explains the diagram Write neatly and use correct English! If the greenhouse effect didn't exist, the average temperature of the earth would decrease from 14C (57F) to the lowest being 18C (04F) There are layers of greenhouse gases Some are carbon dioxide, water vapor, and nitrous oxide These act like a thermal blanket for the Earth They absorb heat and warm the surface for an average of 59




What Is Green House Effect B Draw A Well Labeled Diagram Of Carbon Cycle Brainly In
Find greenhouse effect diagram stock images in HD and millions of other royaltyfree stock photos, illustrations and vectors in the collection Thousands of new, highquality pictures added every day1 Example of student work about exploring the greenhouse effect in garden greenhouses Greenhouse effect (Figure 411) is a sketch of the experiment done in class FIG 411 Student drawing of model of the greenhouse effect in a garden greenhouse The student labeled two lamps shining on two clear plastic tubsSulfur hexafluoride (SF 6) is an extremely potent greenhouse gas SF 6 is very persistent, with an atmospheric lifetime of more than a thousand years Thus, a relatively small amount of SF 6 can have a significant longterm impact on global climate change SF 6 is humanmade, and the primary user of SF 6 is the electric power industry Because of its inertness and dielectric properties, it is
Greenhouse effect and explore natural and humancaused greenhouse gas emissions and their impacts Students will brainstorm and then research natural and human activities that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and draw them in a diagram Students then discuss how they can reduce their contributions to greenhouse gas emissionsGases in the atmosphere can contribute to the greenhouse effect both directly and indirectly Direct effects occur when the gas itself is a greenhouse gas Indirect radiative forcing occurs when chemical transformations of the original gas produce a gas or gases that are greenhouse gases, when a gas influences theComparisons Both processes contribute to Earth's temperature/global warming Same amount of heat energy is produced by the sun & reaches the atmosphere Sun's production of energy is a major role in greenhouse and enhanced greenhouse effect CO2 plays a major role in existence of both processes CO2 & other gases block transmission of long wavelength radiation
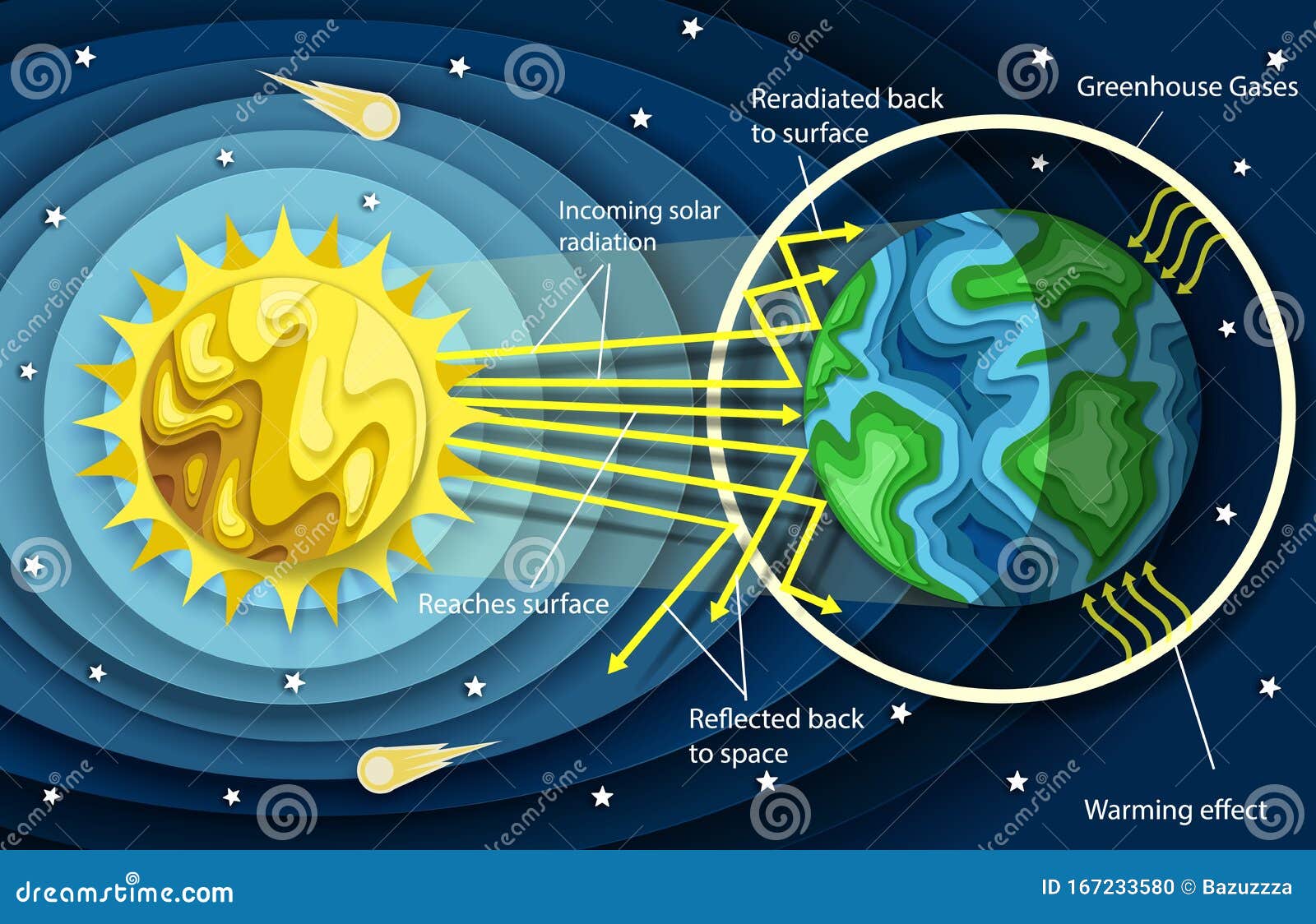
"A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozoneThe greenhouse effect is generally modeled on a macro scale by designating energy balance for the planetary system This involves the incoming solar radiation, reflected solar energy, absorbed solar energy at the ground, and subsequent reradiation at longer wavelengths from the ground The reradiated energy is then either transmitted out of the system or absorbed by the greenhouseFind the perfect Greenhouse Effect Diagram stock photos and editorial news pictures from Getty Images Select from premium Greenhouse Effect Diagram of the highest quality




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Science Classroom Poster Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Global Warming Project
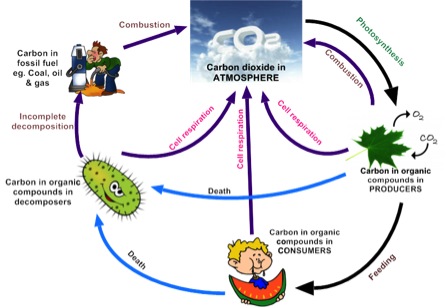
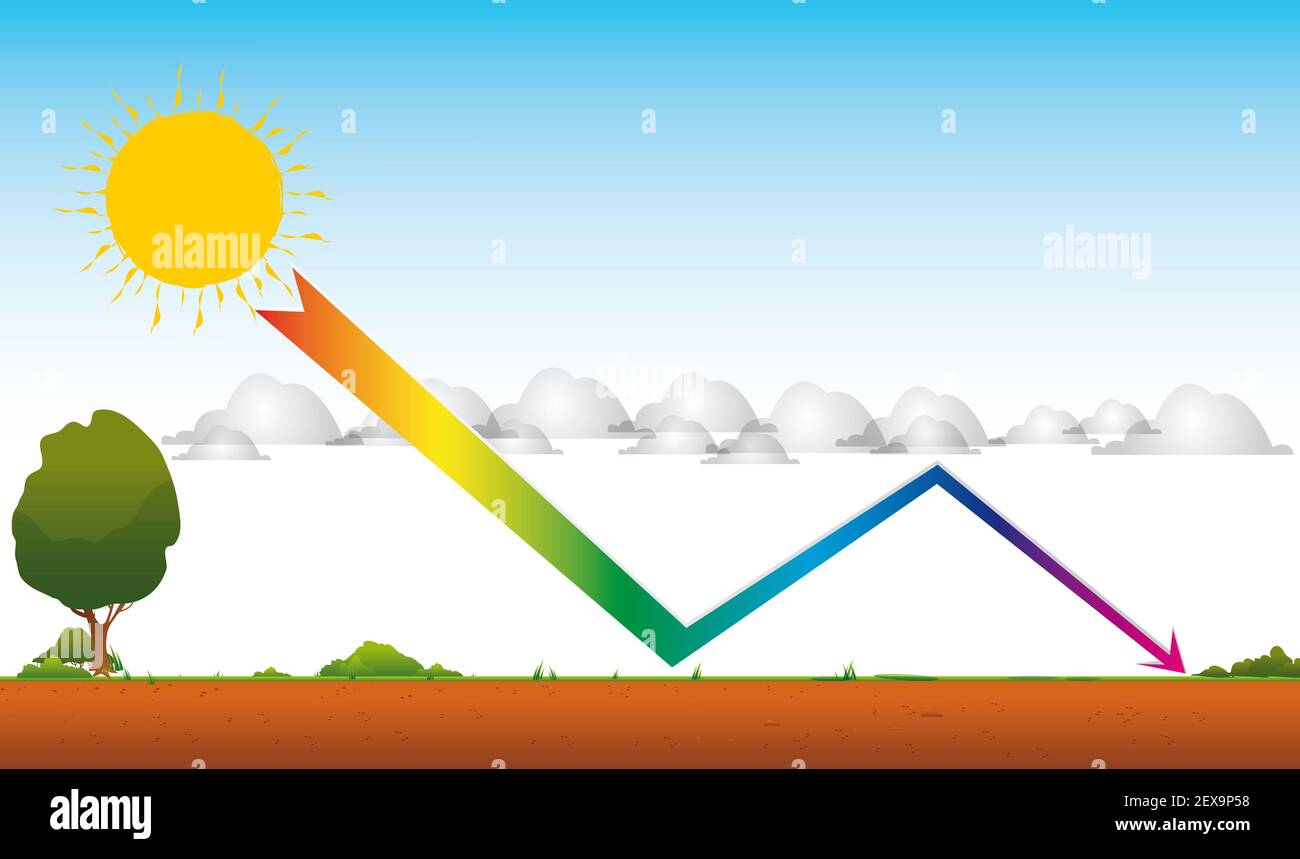
The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surface This warms Earth's surface, and then Earth radiates some of521 Draw and label a diagram of the carbon cycle to show the processes involved 522 Analyse the changes in concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide using historical records 523 Explain the relationship between rises in concentrations of atmospheric carbon dioxide, methane and oxides of nitrogen and the enhanced greenhouse effect




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



The Greenhouse Effect
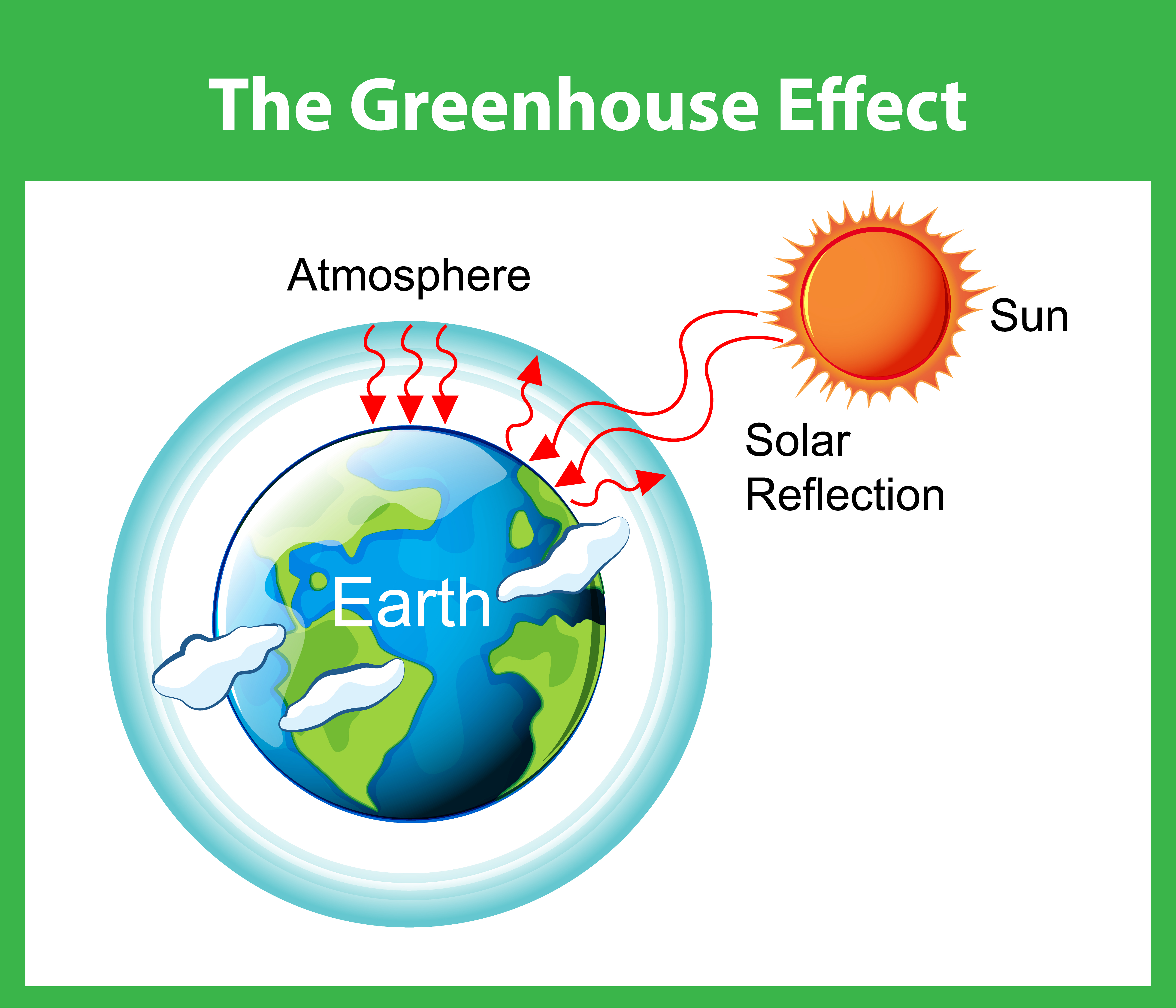
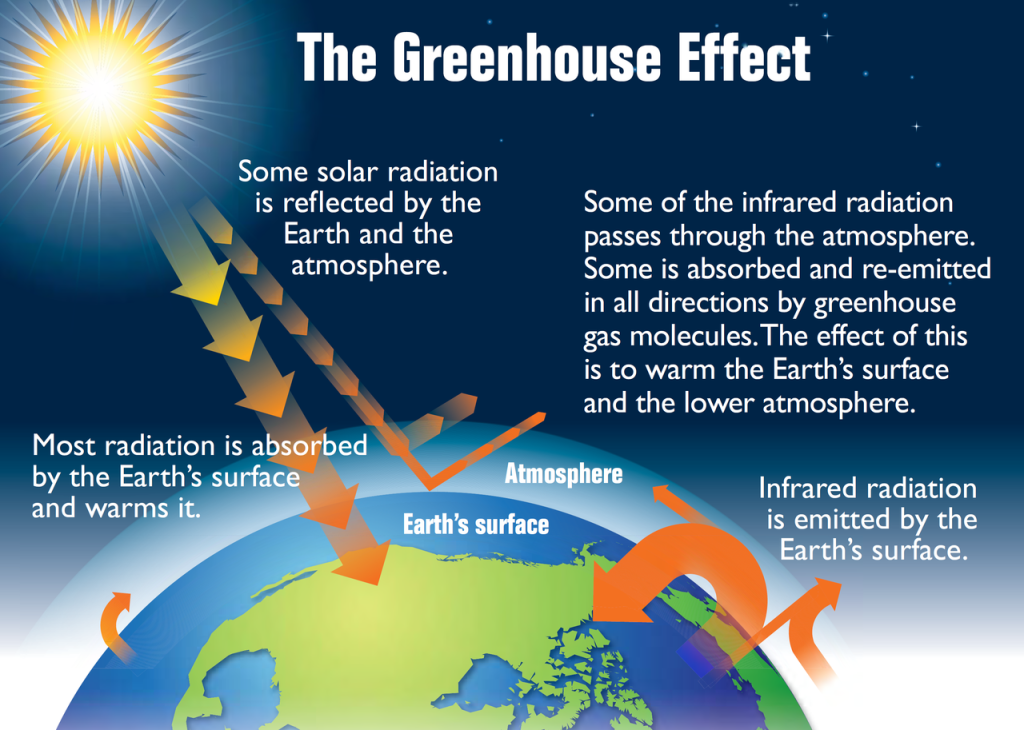
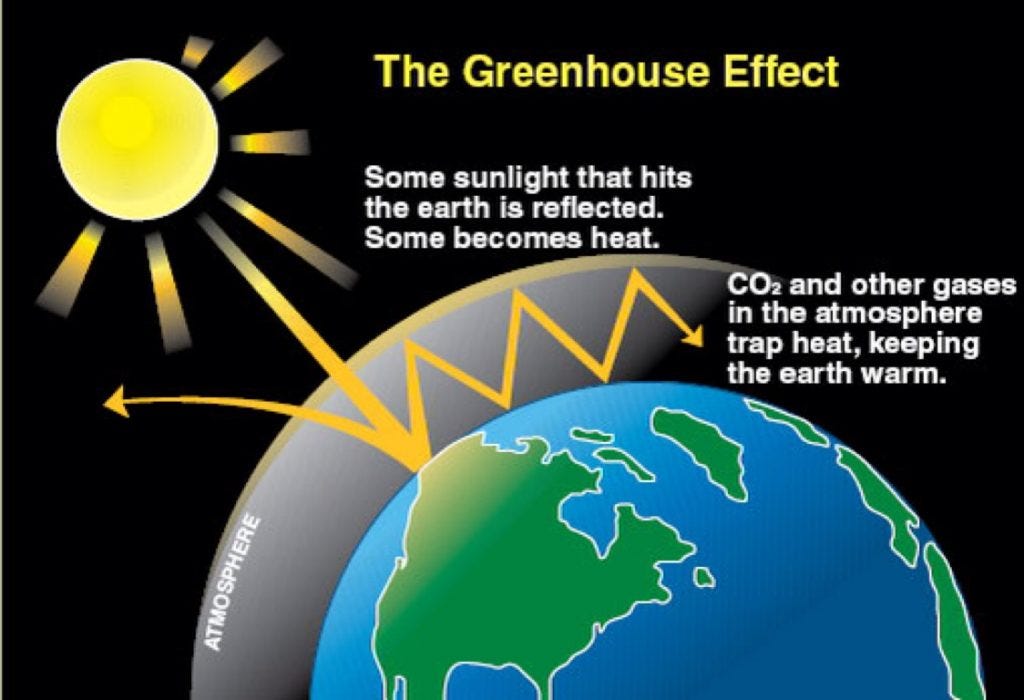
Greenhouse diagram ( Flowchart) Use Creately's easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram, collaborate with others and export results to multiple image formats We were unable to load the diagram You can edit this template and create your own diagram Creately diagrams can be exported and added to Word, PPT (powerpoint), Excel, Visio orThe diagram gives more details about this process, called the greenhouse effect How the greenhouse effect works Electromagnetic radiation at most wavelengths passes through the Earth's atmosphereThe "Greenhouse Effect" A greenhouse is a building made of glass that allows sunlight to enter but traps heat inside, so the building stays warm even when it's cold outside Because gases in the Earth's atmosphere also let in light but trap heat, many people call this phenomenon the "greenhouse effect" The greenhouse effect works



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Biology4ibdp




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids
The greenhouse effect The diagram outlines how the greenhouse effect works Sunlight passes through the Earth's atmosphere The ground warms up and heat is emitted from the Earth's surfaceThis diagram explains to us about the greenhouse effect Basically what greenhouse effect is, is the sun, which emits mostly long radiation and shortwave radiation, all this radiation comes in in the morning or during daytime without any problem The atmosphere, which has various kinds of gases like oxygen, nitrogen, little bit of carbonBrowse 234,977 greenhouse effect stock photos and images available or search for greenhouse effect diagram or greenhouse effect illustration to find more great stock photos and pictures Man on a rooftop looks at approaching flames as the Springs fire continues to grow on near Camarillo, California




The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Download



Greenhouse Gas Vector Art Icons And Graphics For Free Download
Energy resources diagram "Consumption of energy resources, (eg turning on a light) requires resources and has an effect on the environment Many electric power plants burn coal, oil or natural gas in order to generate electricity for energy needs While burning these fossil fuels produces a readily available and instantaneous supply ofForm definitions of the greenhouse effect based on prior knowledge, class discussion, and viewing diagrams 2 Participate in group brainstorming sessions and class discussions related to the impact of the greenhouse effect and global warming 3 Analyze global warming diagrams and resources to obtain a clear understanding of this scientificThe greenhouse effect of Venus From geometry, we can calculate the average solar flux over the surface of Venus It is approximately 661 W/m2 Venus is very reflective of solar radiation In fact, it has a reflectivity (or albedo) of 08, so the planet absorbs approximately 661 X 02 = 132 W/m2 By assuming that the incoming radiation equals the




Atmosphere Climate Environment Information Programme




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases
Drawing shows four different levels of ozone in the atmosphere At top of stratosphere, 30 miles high, ozone absorbs most of the harmful ultraviolet radiation from the Sun At the top of the troposphere, 12 miles high, ozone acts as a greenhouse gas, trapping heatWHAT IS THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life Human action, however, has increased the presence of theseActivity 11 Understanding the Greenhouse Effect Grades 7 – 9 Description In Part 1 Modeling the Greenhouse Effect, students will do a lab that demonstrates the greenhouse effect, and will discuss the results of the lab In Part 2 The Earth's Energy Balance, students will color in a diagram, answer opinion




What Is Green House Effect B Draw A Well Labeled Diagram Of Carbon Cycle Brainly In




Greenhouse Effect High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
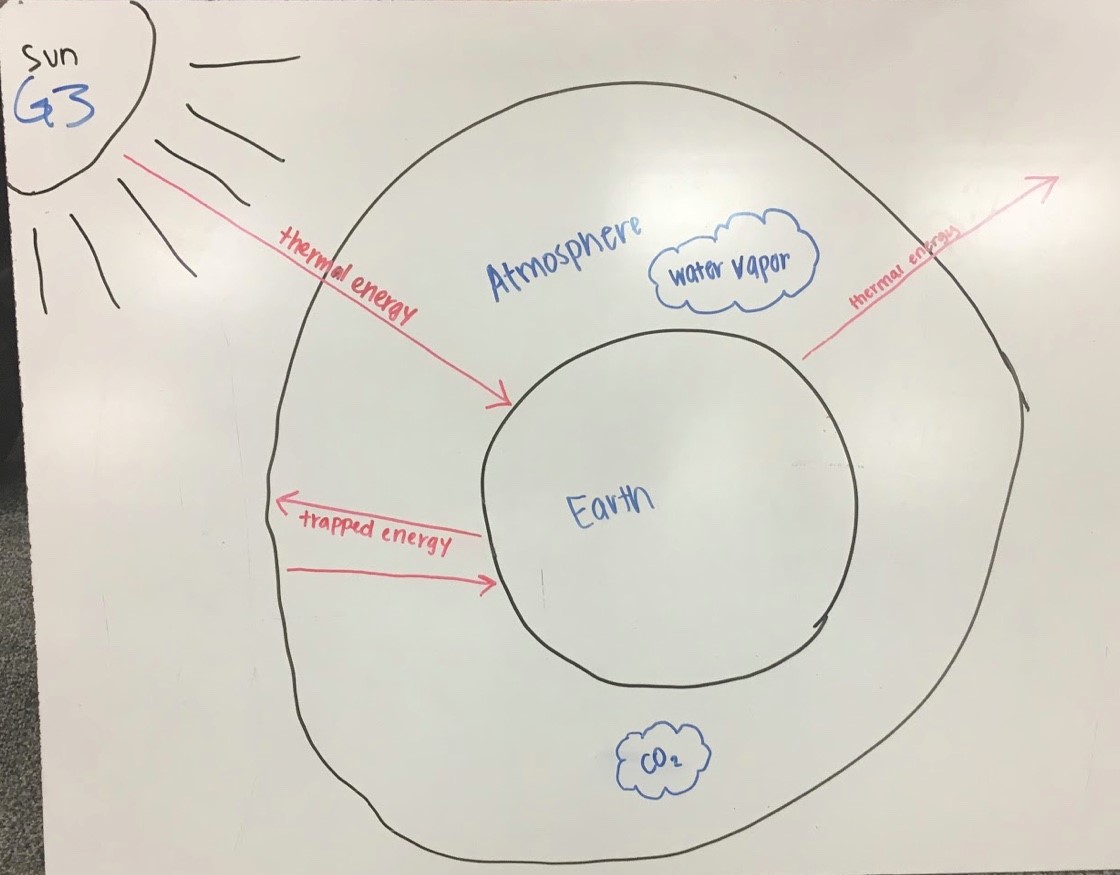
Create your own unique sketch illustrating how Earth's Greenhouse Effect works You may handdraw your diagram or create something on the computer Either option must be a unique creation (ie DO NOT COPY & PASTE) If you choose to handdraw your diagram you will need to scan and upload your diagram into BlackboardUse the back of this worksheet if necessary Graphic A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect Perhaps the most impressive of cloud formations, cumulonimbus (from the Latin for "pile" and "rain cloud") clouds form due to vigorous convection (rising and overturning) of warm, moist and unstable air




What Is Green House Effect B Draw A Well Labeled Diagram Of Carbon Cycle Brainly In



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau
Diagram Of Greenhouse Effect Saved by Yasar alp Ozturk 1 Greenhouse Effect Heat Energy Red Glass Worksheets Diagram ArchitectureIT adds to the greenhouse effect Draw a diagram and label to EXPLAIN the greenhouse effect Explain how the Carbon Cycle is involved in global climate change Carbon is continuously exchanged and recycled among the reservoirs through natural processes As plants photosynthesize during the growing season, they remove large amounts of CO2 fromHave students create a diagram depicting the Greenhouse Effect using paper, markers, etc Tell them that they will be asked to go home and explain the Greenhouse Effect and global warming to a family member using their diagram as part of a homework assignment Have them practice presenting global warming using their diagrams with peer partners



The Greenhouse Effect




Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect A Scientific Infographic
Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapor has the largest effectA greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas in the atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozoneThe greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to exist



1




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
Greenhouse effect diagram can either be printed off or projected and used to explain the Greenhouse effectGreenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climate change since the mid th century 1 The indicators in this chapter characterize emissions of the major greenhouse gases resulting from human activities, the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere, and how emissions and concentrations have changed over timeGreenhouse celebrates Pride Buy a shirt, help an LGBTQ teen We're shining a spotlight on the LGBTQ community with our new Pride tshirt 100% of the proceeds are going to support The Trevor Project and the Ali Forney Center



How Does The Greenhouse Effect Keep The Earth Warm Socratic



Free Greenhouse Gases Cliparts Download Free Greenhouse Gases Cliparts Png Images Free Cliparts On Clipart Library
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, trapThe Greenhouse Effect Click Here for Transcript of The Greenhouse Effect video This diagram explains to us about the greenhouse effect Basically what greenhouse effect is, is the sun, which emits mostly long radiation and shortwave radiation, all this radiation comes in in the morning or during daytime without any problem




Nasa S Climate Kids What Is The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Earth Science Homeschool Current Events For Kids
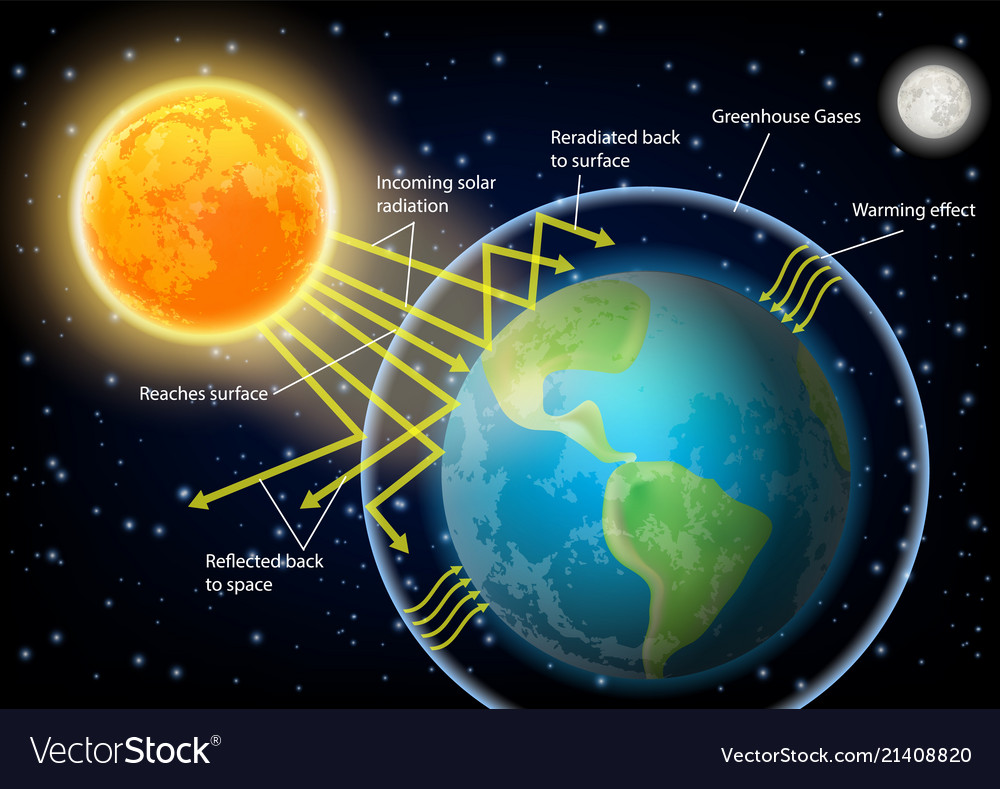



Greenhouse Effect Diagram Royalty Free Vector Image
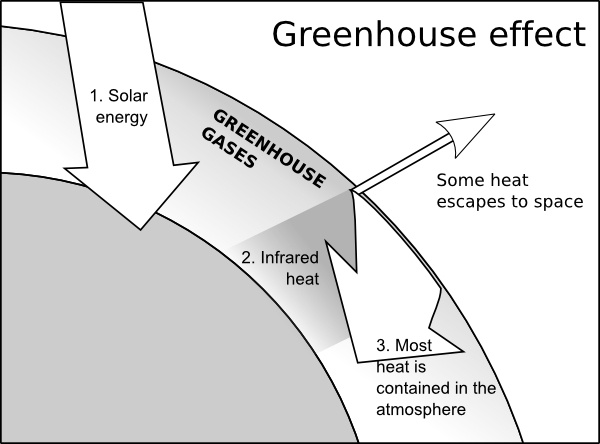



Greenhouse Effect Clip Art Free Vector In Open Office Drawing Svg Svg Vector Illustration Graphic Art Design Format Format For Free Download 552 86kb




Textbook Representation Of The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Layer Download Scientific Diagram



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature




Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect
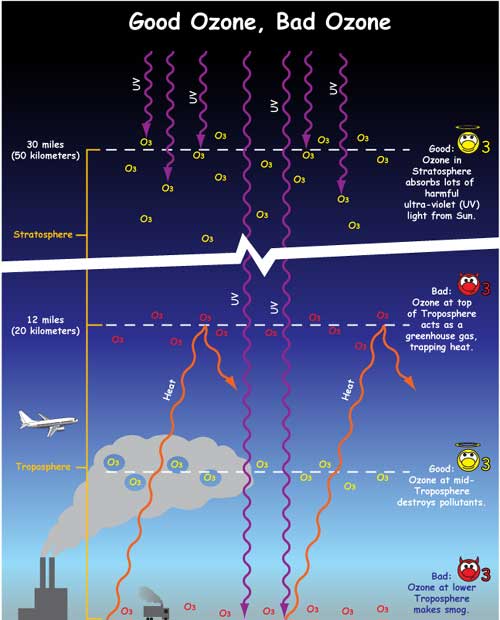



The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
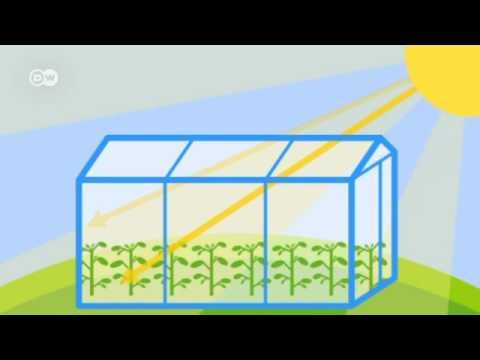



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Ideas Youtube




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Ciencias Naturales Ciencia Dieta Balanceada
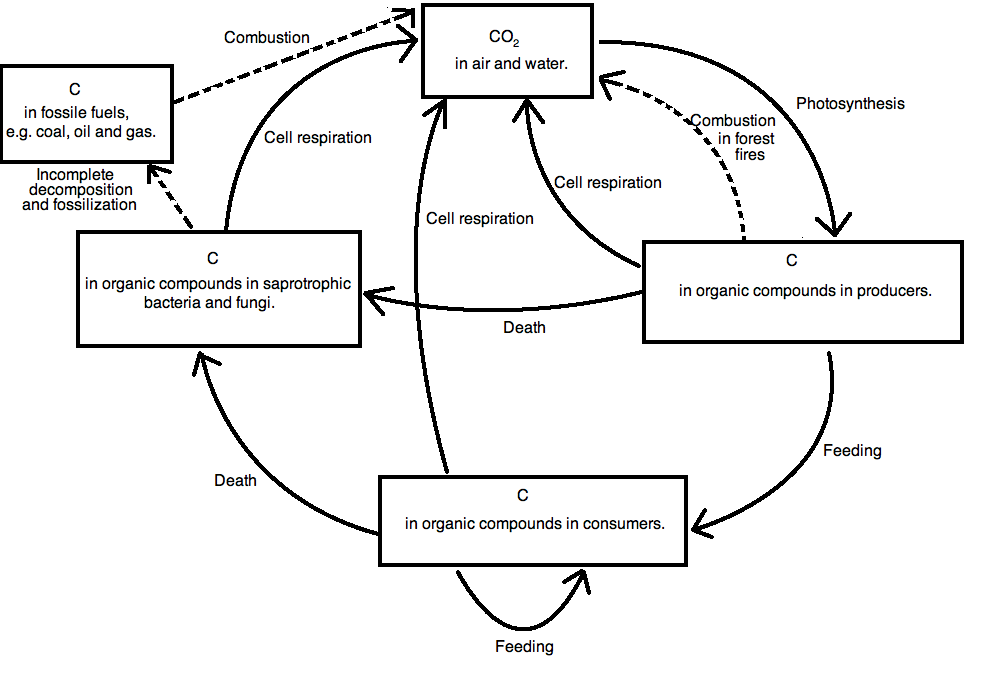



Ib Biology Notes 5 2 The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Diagram Of Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Diagram




Greenhouse Effect Vs Global Warming Drawing Easy Drawing For Kids Youtube



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena




Green House Drawing For Kids Novocom Top




How To Explain The Greenhouse Effect To Kids With Printables Kidminds




The Diagram Given Shows The Green House Effect Which Of The Following Would Have Been In The Absence Of Greenhouse Effect In The Atmosphere




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica



The Greenhouse Effect



The Greenhouse Effect



Greenhouse Effect Advantages And Disadvantages By Tutorbin Medium



Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena



Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 154 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Greenhouse Gases Easy Drawing Novocom Top
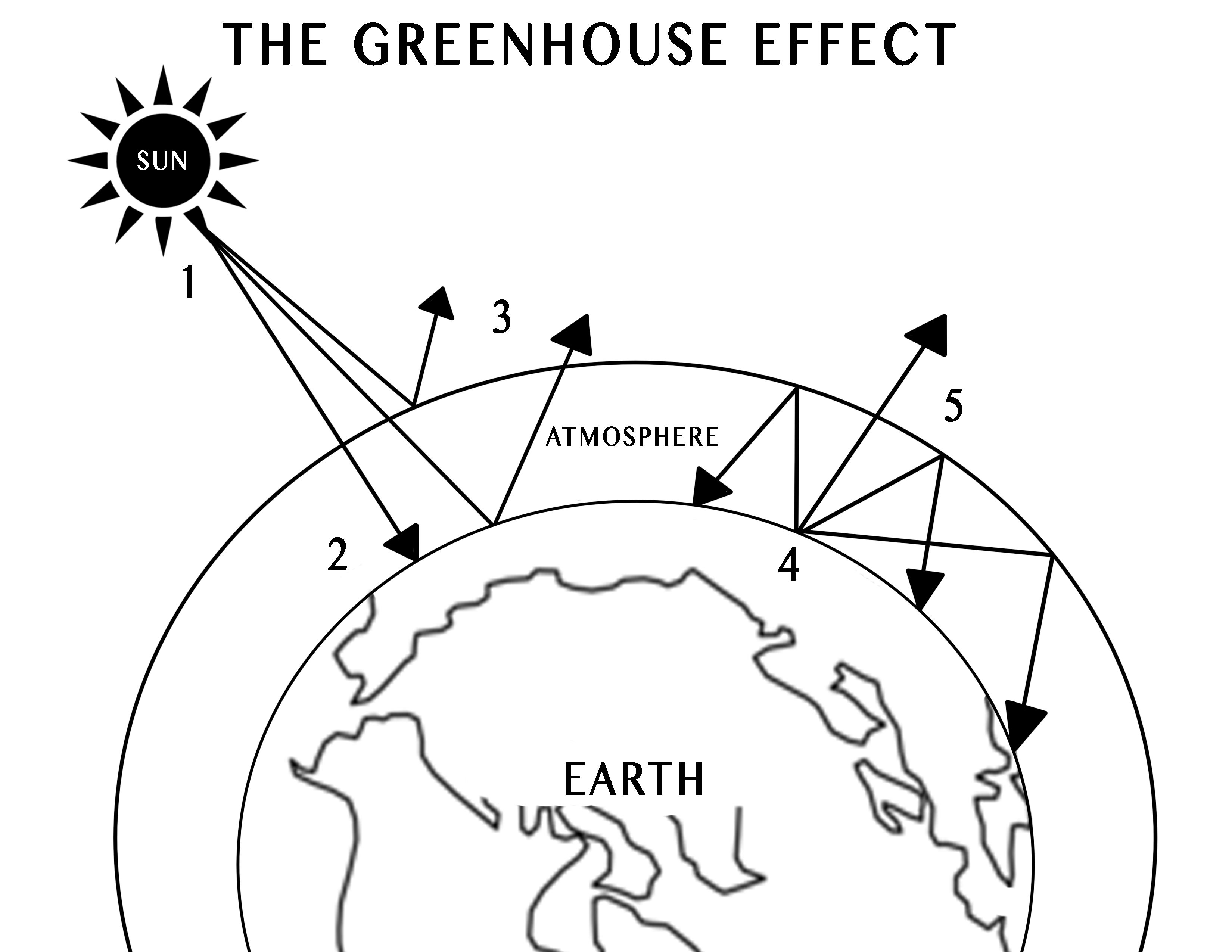



Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena




How To Draw A Diagram Of Green House Effect Global Warming Easy Youtube




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau




Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock



The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
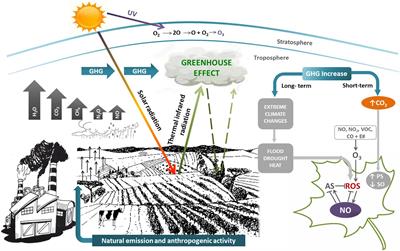



Frontiers Climate Change And The Impact Of Greenhouse Gasses Co2 And No Friends And Foes Of Plant Oxidative Stress Plant Science



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja
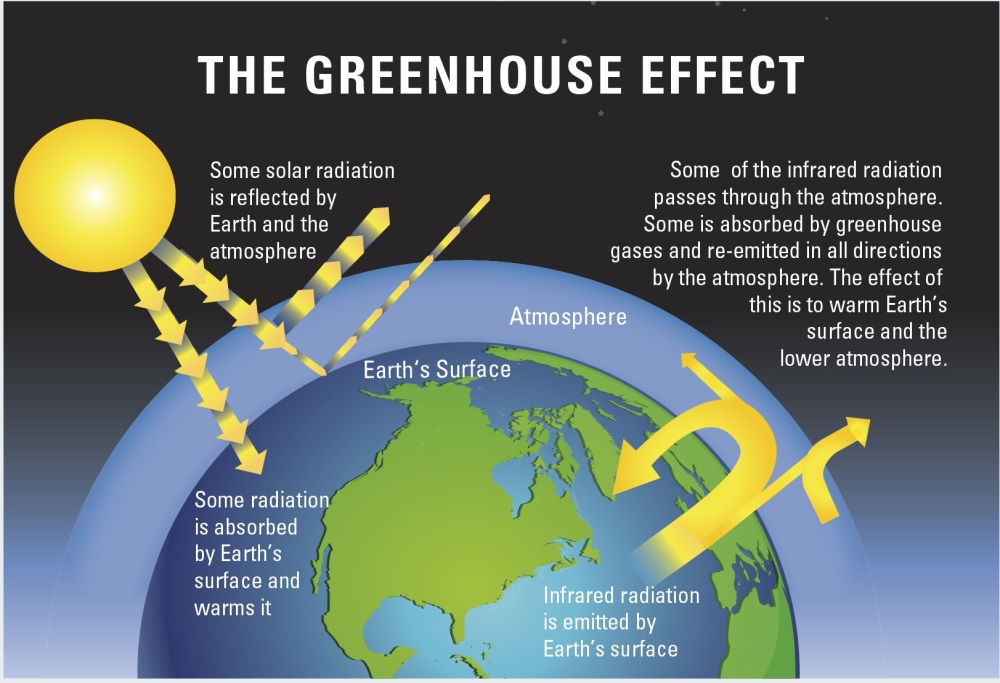



What Is The Relationship Between Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Socratic




How To Draw A Diagram Of Green House Effect Global Warming Easy Youtube
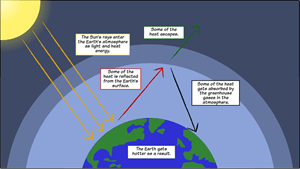



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube
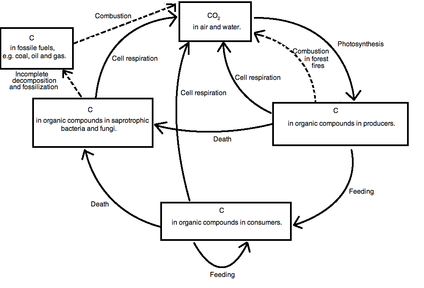



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Biology4ibdp



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Climate Change Silence Is Ignorance Really Bliss Early Career Ecologists
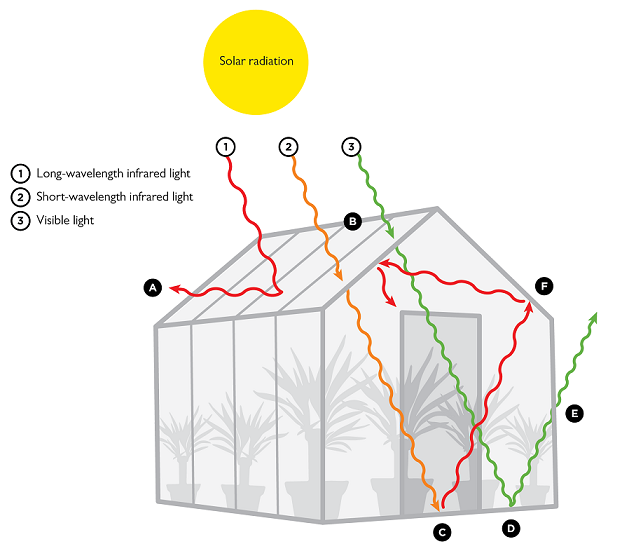



The Greenhouse Effect Comsol Blog



Free Greenhouse Gases Cliparts Download Free Greenhouse Gases Cliparts Png Images Free Cliparts On Clipart Library
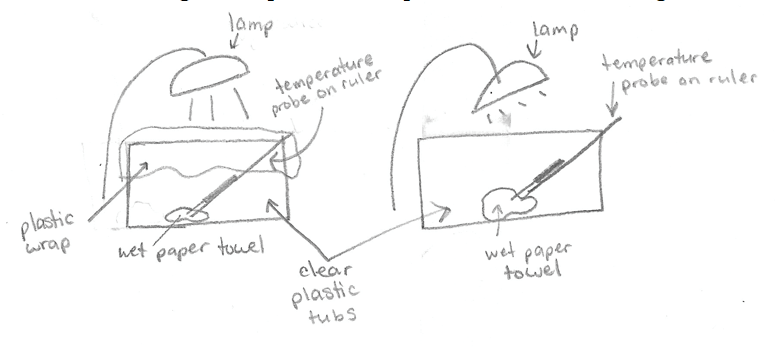



Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students



Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia



Q Tbn And9gctaj8wii876qu Vg Qiwf0vbxzn5m2dj2uyfahncczk01qi3 Z7 Usqp Cau



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




The Greenhouse Effect Explained



Carbon Cycle And Green House Samantha Sihakoun A P Environmental Science




Drawing Of Greenhouse With Glass Walls And Roof Plants Growing Inside Sunlight Coming In Through Roof But B Greenhouse Effect Green House Effect Greenhouse




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
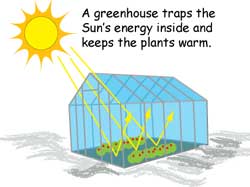



The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids



The Greenhouse Effect




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature




Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect A Scientific Infographic




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




Greenhouse Effect Aumsum Kids Science Education Children Youtube
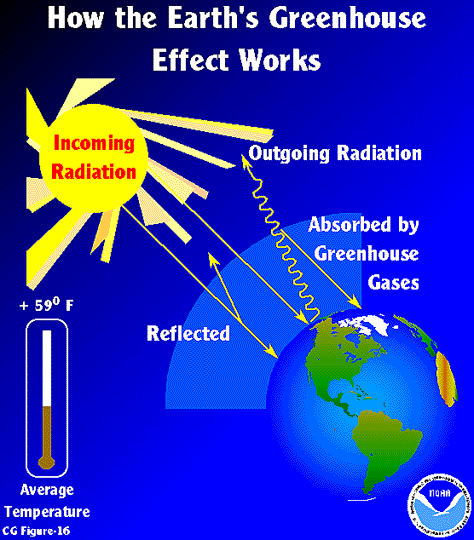



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach



Www Chicagobotanic Org Downloads Nasa Unit 1 Grades 7 9 Activity 1 3 Greenhousegasesnaturalandhumancauses Pdf




Greenhouse Effect High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Greenhouse Effect Starter Draw What You Think Teaching Resources
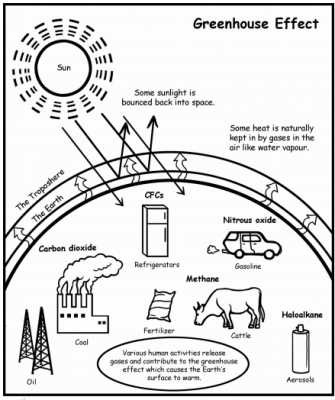



Greenhouse Effect Clever Cookies




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects
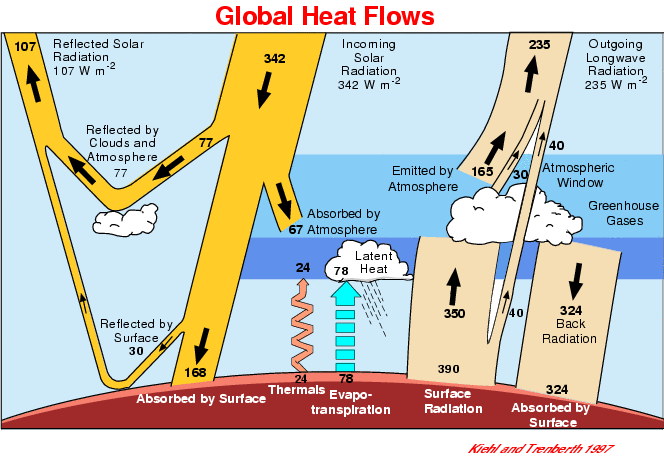



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect




Greenhouse Effect Illustrations And Clipart 2 293 Greenhouse Effect Royalty Free Illustrations And Drawings Available To Search From Thousands Of Stock Vector Eps Clip Art Graphic Designers
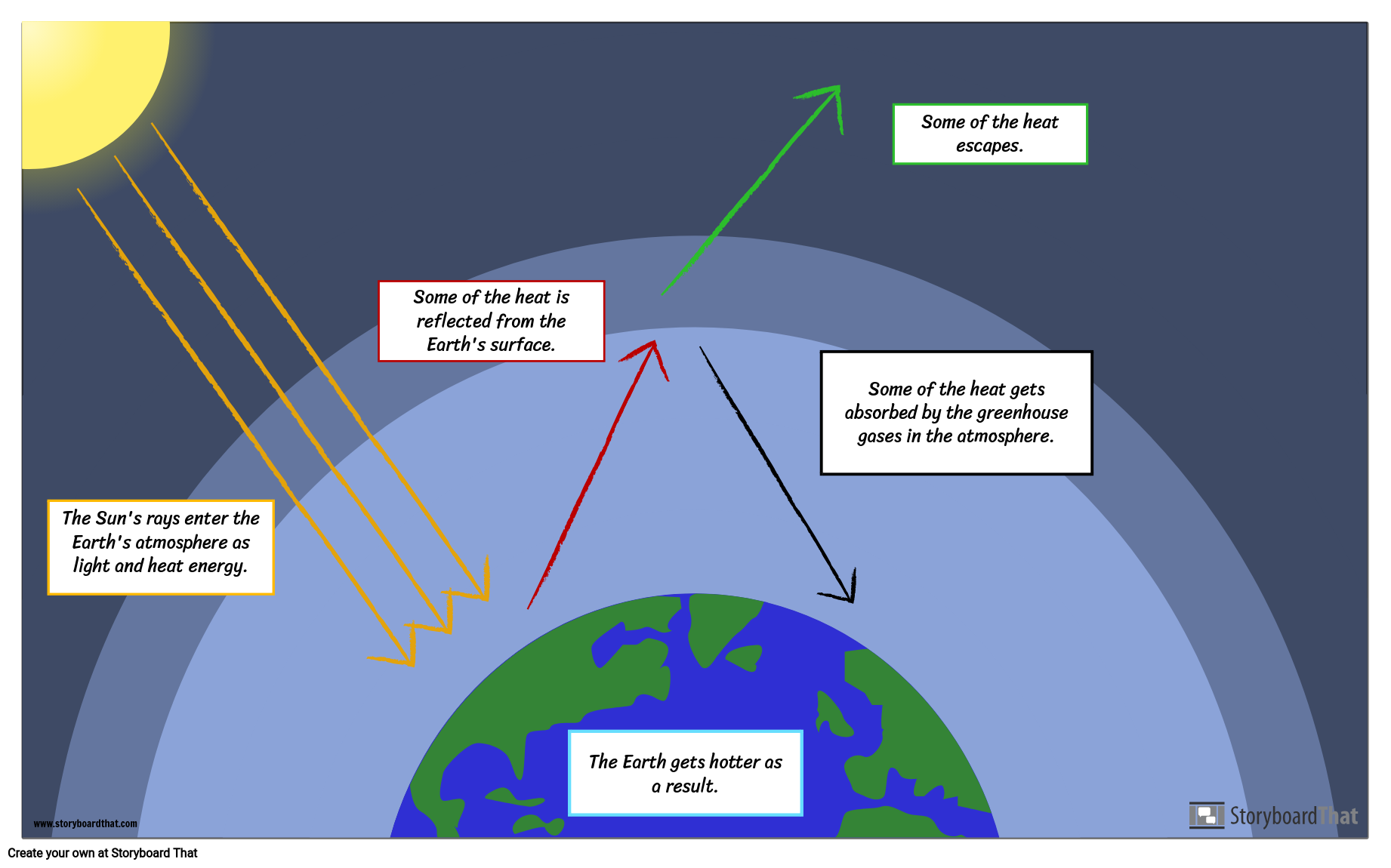



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram
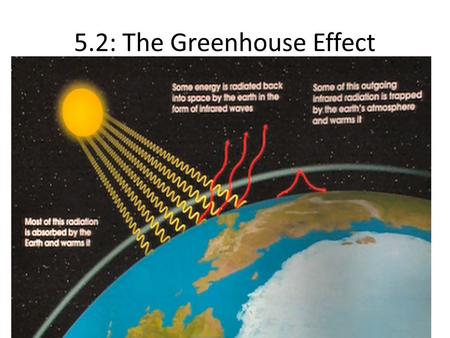



The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Download




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Best Greenhouse Effect Ideas Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse What Is A Conservatory




4 2 The Greenhouse Effect A Biology



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿